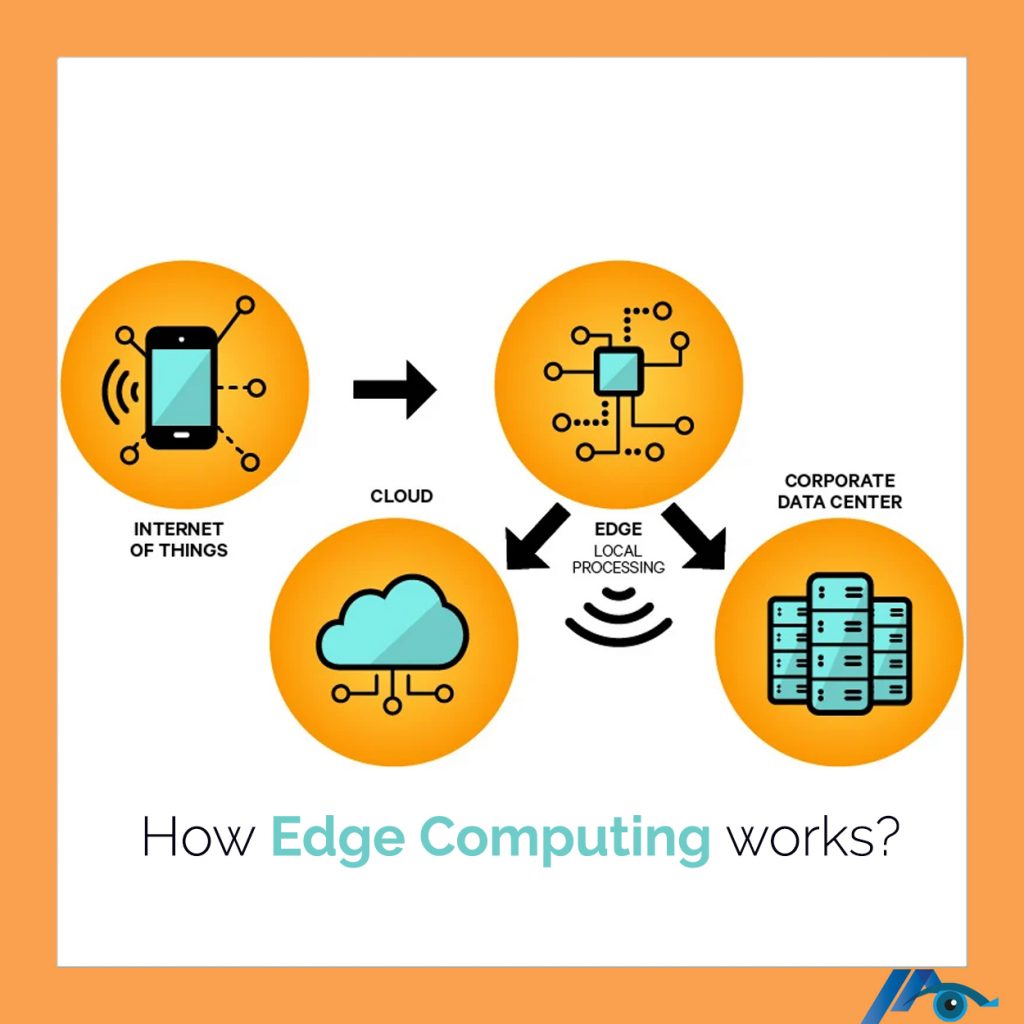
In the modern era of rapid digital transformation, the amount of data generated by devices, users, and systems is growing exponentially. This data explosion demands faster processing, reduced latency, and more efficient data management. Traditional cloud computing, while powerful, has limitations when it comes to handling these demands in real time. This is where edge computing comes into play. Edge computing is a distributed computing paradigm that brings computation and data storage closer to the location where it is needed, thereby improving response times and saving bandwidth.
At its core, edge computing decentralizes computing resources, shifting them from centralized data centers to the “edge” of the network — often directly onto devices like smartphones, sensors, or local servers. The idea is to process data locally rather than sending it across long routes to central data centers. This enables quicker decisions, reduced latency, and more efficient use of bandwidth. For example, in a self-driving car, sensors collect enormous amounts of data every second. Sending this data to a cloud server for analysis and then waiting for a response is impractical due to latency issues. Edge computing allows such data to be processed within the vehicle, enabling real-time reactions that are critical for safety.
Benefits of Edge Computing
Reduced latency
One of the key benefits of edge computing is reduced latency. Latency is the delay between a user’s action and the system’s response. In applications like online gaming, remote surgery, or augmented reality, even a delay of a few milliseconds can lead to failures or suboptimal experiences. By moving computation closer to the user or device, edge computing drastically cuts down on this delay, ensuring smoother and more reliable performance.
Bandwith Optimization
Another major advantage is bandwidth optimization. With the rise of the Internet of Things (IoT), billions of devices are constantly transmitting data. Continuously sending this data to cloud servers can consume enormous bandwidth, leading to congestion and higher costs. Edge computing helps by filtering and processing data locally. Only relevant or summarized information is sent to the cloud, significantly reducing the bandwidth needed.
Enhanced security and privacy
This is an additional strengths of edge computing. When sensitive data is processed locally rather than transmitted across networks, there is a lower risk of interception or breaches. This is particularly crucial in fields such as healthcare, finance, and defense, where data confidentiality is paramount. However, it is important to note that edge devices themselves must be secure, as their decentralization can make them vulnerable to physical and cyber attacks if not properly managed.
Scalability
Edge computing also supports scalability. In industries such as manufacturing, smart cities, and retail, edge devices can be deployed at scale to handle localized computing needs. For instance, in a smart factory, sensors and controllers can monitor equipment health, energy usage, and environmental conditions in real time. Instead of relying on a central system to analyze this data, edge computing enables each part of the factory to make decisions independently, increasing efficiency and reducing downtime.
Challenges
Despite its advantages, edge computing comes with challenges. Device management and maintenance can be complex, especially when thousands of edge devices are deployed in various locations. Ensuring that each device is updated, secure, and functioning correctly requires robust management systems. Moreover, data consistency can become an issue when multiple edge nodes operate independently. Coordinating data across these nodes and syncing with cloud infrastructure demands careful planning and reliable communication protocols.
Edge computing is not meant to replace cloud computing; rather, it complements it. The cloud still plays a vital role in data storage, large-scale analytics, and centralized control. Edge computing is ideal for time-sensitive tasks and preliminary data processing, while the cloud can handle deeper analysis and long-term storage. Together, they form a hybrid architecture that combines the strengths of both paradigms.
Examples of Edge Computing:
- IoT Devices: Processing data from sensors in smart homes, industrial settings, or vehicles.
- Smart Cities: Managing traffic, optimizing energy usage, and providing real-time services.
- Self-Driving Cars: Enabling real-time decision-making and navigation based on sensor data.
- Automated Industries: Monitoring equipment, detecting failures, and optimizing production lines.
- Mobile Networks: Delivering content and services to users with lower latency.
Conclusion
In conclusion, edge computing represents a significant shift in how data is processed and managed. By bringing computation closer to the source of data generation, it reduces latency, optimizes bandwidth usage, enhances security, and improves real-time decision-making. As technologies like IoT, artificial intelligence, and 5G continue to grow, the relevance and impact of edge computing will only increase. Organizations that embrace this paradigm will be better positioned to handle the demands of the digital future, delivering faster, smarter, and more secure services to users around the globe.
Miracle technologies is a comprehensive NYC based Managed IT Services for Business IT Infrastructures. Our platform is built upon years of unmatched experience at AT&T Labs Research and renowned Wall Street MSPs. We offers cloud support, data center support, C suite services, backbone servers support, security servers, 24/7 managed IT support and Business Continuity/Disaster Recovery.